Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are painful, swollen veins in the lower portion of the rectum or anus.
Causes
Hemorrhoids are very common, especially during pregnancy and after childbirth. They result from increased pressure in the veins of the anus. The pressure causes the veins to swell, making them painful, particularly when you are sitting.
The most common cause is straining during bowel movements.
Hemorrhoids may be caused by:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Constipation
- Sitting for long periods of time
- Anal infections
- Certain diseases, such as liver cirrhosis
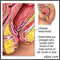
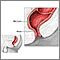
Hemorrhoids may be inside or outside the body.
- Internal hemorrhoids occur just inside the anus, at the beginning of the rectum. E
- External hemorrhoids occur at the anal opening and may hang outside the anus.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hemorrhoids include:
- Anal itching
- Anal ache or pain, especially while sitting
- Bright red blood on toilet tissue, stool, or in the toilet bowl
- Pain during bowel movements
- One or more hard tender lumps near the anus
Exams and Tests
A doctor can often diagnose hemorrhoids simply by examining the rectal area. If necessary, tests that may help diagnose the problem include:
- Stool guaiac (shows the presence of blood)
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Anoscopy
Treatment
Treatments for hemorrhoids include:
- Over-the-counter corticosteroid creams to help reduce pain and swelling
- Hemorrhoid creams with lidocaine to help reduce pain
- Stool softeners help reduce straining and constipation
Witch hazel (applied with cotton swabs) can reduce itching. Other steps to reduce this itching include:
- Wear cotton undergarments.
- Avoid toilet tissue with perfumes or colors, use baby wipes instead.
- Try not to scratch the area.
Sitz baths can help you to feel better. Sit in warm water for 10 to 15 minutes.
If your hemorrhoids do not get better with home treatments, you may need a type of heat treatment to shrink the hemorrhoids. This is called infrared coagulation. This may help avoid surgery.
Surgery that may be done to treat hemorrhoids includes rubber band ligation or surgical hemorrhoidectomy. These procedures are generally used for patients with severe pain or bleeding who have not responded to other therapy.
Possible Complications
The blood in the swollen vein may form clots, and the surrounding tissue can die. Surgery is often needed to remove hemorrhoids with clots.
Severe bleeding may also occur. Iron deficiency anemia can result from long-term blood loss. Significant bleeding from hemorrhoids is unusual, however.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call for your health care provider if hemorrhoid symptoms do not improve with home treatment. You should also be seen if you have rectal bleeding. Your provider may want to check for other, more serious causes of the bleeding.
Call 911 if you lose a lot of blood, or if you are bleeding and feel dizzy, lightheaded, or faint.
Prevention
Constipation and straining during bowel movements raise your risk for hemorrhoids. To prevent constipation and hemorrhoids, you should:
- Drink plenty of fluids, at least eight glasses per day.
- Eat a high-fiber diet of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Consider fiber supplements.
- Use stool softeners to prevent straining.
Alternative Names
Rectal lump; Piles; Lump in the rectum
References
Sneider EB, Maykel JA. Diagnosis and management of symptomatic hemorrhoids. Surg Clin North Am. 2010 Feb;90(1):17-32, Table of Contents.
Nelson H, Cima RR. Anus. In: Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 51.
Update Date: 5/16/2012
Reviewed by: Todd Eisner, MD, Private practice specializing in Gastroenterology, Boca Raton, FL. Clinical Instructor, Florida Atlantic University School of Medicine. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.