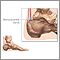
Retrocalcaneal bursitis
Retrocalcaneal bursitis is swelling (inflammation) of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) under the Achilles tendon.
Causes
A bursa acts as a cushion and lubricant between tendons and muscles sliding over bone. There are bursas around most large joints in the body, including the ankle.
The retrocalcaneal bursa is located in the back of the ankle by the heel. It is where the large Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Repeated or too much use of the ankle can cause this bursa to become irritated and inflamed. Possible causes are too much walking, running, or jumping.
This condition is usually linked to Achilles tendinitis. Sometimes retrocalcaneal bursitis may be mistaken for Achilles tendinitis.
Risks for this condition include starting an aggressive workout schedule, or suddenly increasing activity level without the right conditioning.
Symptoms
- Pain in the heel, especially with walking, running, or when the area is touched
- Pain may get worse when rising on the toes (standing on tiptoes)
- Red, warm skin over the back of the heel
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will take a history to find out if you have symptoms of retrocalcaneal bursitis. Examining your ankle can find the location of the pain. The physician will look for tenderness and redness in the back of the heel.
The pain may be worse when the doctor bends the ankle upward (dorsiflex). Or, the pain may be worse when you rise on your toes.
You will not usually need imaging studies such as x-ray and MRI at first. If the first treatment does not improve the symptoms, your health care provider may recommend these tests. MRI may show inflammation.
Treatment
Your health care provider may recommend the following treatments:
- Avoid activities that cause pain.
- Ice the heel several times a day.
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (for example, ibuprofen).
- Try over-the-counter or custom heel wedges to help decrease the stress on the heel.
- Try ultrasound treatment during physical therapy to reduce inflammation.
- Use physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength around the ankle, which can help the bursitis improve and prevent it from coming back.
If these treatments don't work, your health care provider may inject a small amount of steroids into the bursa. After the inection, you should avoid stretching the tendon too much because it can break open (rupture).
If the condition is connected with Achilles tendinitis, casting the ankle for several weeks to keep it from moving can be effective. Very rarely, surgery may be needed to remove the inflamed bursa.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This condition usually gets better in several weeks with the proper treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications are rare. If the bursitis occurs with tendinitis, tendon rupture is possible. Tendon rupture may also occur with steroid injections, especially if they are given too often.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you have heel pain or symptoms of retrocalcaneal bursitis that do not improve with rest, contact your health care provider for evaluation and treatment.
Prevention
Maintain proper form when exercising, as well as good flexibility and strength around the ankle to help prevent this condition.
Proper stretching of the Achilles tendon helps prevent injury.
Alternative Names
Insertional heel pain
References
Wapner KL, Parekh SG. Heel pain. In: DeLee JC, Drez D Jr., Miller MD, eds. DeLee and Drez's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier;2009:section F.
Aranow MS. Posterior heel pain (retrocalcaneal bursitis, insertional and noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy). Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2005;22:19-43.
Updated: 4/31/2012
Reviewed by: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Assistant Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.