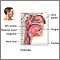
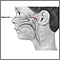
Enlarged adenoids
Enlarged adenoids is swelling of the lymph tissue found in the airway between your nose and the back of your throat. The tissue is similar to the tonsils.
Causes
Enlarged adenoids may be a natural occurrence, beginning when the baby grows in the womb.
Long-term inflammation can also lead to englarged adenoids.
The adenoids normally shrink as a child grows older.
Symptoms
- Bad breath
- Cracked lips
- Dry mouth
- Mouth breathing (mostly at night)
- Mouth open during day (more severe obstruction)
- Persistent runny nose or nasal congestion
- Restlessness while sleeping
- Snoring
Exams and Tests
The adenoids cannot be seen by looking in the mouth directly, but can be seen with a special mirror or using a flexible endoscope through the nose.
Tests may include:
- X-ray (side view of the throat)
- Sleep apnea studies (severe cases only)
Treatment
Antibiotics may be used to treat tonsil, adenoid, and sinus infections when they occur.
Surgery to remove the adenoids (adenoidectomy) may relieve symptoms or prevent complications in those with frequent ear or sinus infections or fluid behind the ears. It may also be done when ear tubes have not successfully reduced infections.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Full recovery is expected.
Possible Complications
- Frequent ear infections
- Intermittent sleep apnea
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if your child has difficulty breathing through the nose or other symptoms of enlarged adenoids.
Prevention
Treating throat infections early may prevent the adenoids from becoming enlarged from long-term infection and inflammation. Removing the adenoids prevents long-term airway blockage.
Alternative Names
Adenoids - enlarged
References
Wetmore RF. Tonsils and adenoids. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007:chap 380.
Updated: 4/12/2012
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Topics
Images
Read More
Patient Instructions
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.