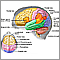
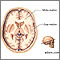
White matter of the brain
The white matter of the brain contains nerve fibers. Many of these nerve fibers (axons) are surrounded by a type of fat called myelin. The myelin gives the whitish appearance to the white matter. Myelin acts as an insulator, and it increases the speed of transmission of all nerve signals.
References
Bhatia PG, Sklar EML. Neuroimaging: structural neuroimaging. In: Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, eds. Bradley: Neurology in Clinical Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Butterworth-Heinemann Elsevier; 2008:chap 36A.
Update Date: 2/16/2012
Reviewed by: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.