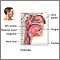
Swallowing difficulty
Difficulty with swallowing is the sensation that food is stuck in the throat, or from the neck down to just above the abdomen behind the breastbone (sternum).
Considerations
Swallowing is a complex act that involves the mouth, throat area, and esophagus (the muscular tube that moves food to the stomach). Many nerves and muscles control how these body parts work. Part of the act of swallowing is under voluntary control, which means you are aware of controlling the action. However, much of swallowing is involuntary.
 Watch this video about:Swallowing
Watch this video about:Swallowing
Problems at any point -- from chewing food and moving it into the back of the mouth to transporting food down the esophagus into the stomach -- can result in difficulty swallowing.
Chest pain, the feeling of food stuck in the throat, or heaviness or pressure in the neck or upper or lower chest when eating are frequently the result of swallowing difficulties.
Causes
There are many different causes of swallowing difficulty, including:
- A blockage due to:
- Cervical spine disease
- Emotional or anxiety disorder
- Esophageal webs
- Narrowings (strictures) due to radiation, chemicals, medications, chronic inflammation, or ulcers
- Schatzki's ring
- Tumors
- Zenker's diverticulum
- Nerve and muscle problems such as:
- Achalasia
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease)
- Esophageal spasm
- Infections such as syphilis
- Myasthenia gravis
- Muscular dystrophy
- Multiple sclerosis
- Nutcracker esophagus
- Parkinson's disease
- Polymyositis
- Scleroderma
- Stroke
Home Care
Eat slowly, and chew food thoroughly. If a person suddenly shows signs of choking and difficulty breathing, food could be blocking the main airway (trachea). The Heimlich maneuver should be performed immediately.
You may have an easier time swallowing liquids or pureed foods than solids. Avoid very cold or very hot foods if you notice that they worsen the problem.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your doctor right away if:
- You cough or have a fever or shortness of breath
- You are losing weight
- Your swallowing problems are getting worse
Call your health care provider if the problem continues, even if the symptoms come and go.
Tell your doctor about any other symptoms you may have including:
- Abdominal pain
- Chills
- Cough
- Heartburn
- Nausea
- Sour taste in mouth
- Weight loss
- Wheezing
- Vomiting, especially if it contains blood
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask questions about your medical history and symptoms, including:
- Do you have difficulty swallowing solids, liquids, or both?
- Do you cough or choke during or after eating?
- Do you have a weak voice?
- Is the problem constant or does it come and go?
- Is it getting worse?
- Does it hurt to swallow? Do you have chest discomfort when you swallow?
- Does it feel like you have a lump in your throat?
- Have you breathed in or swallowed any irritating substances?
- Are you losing any weight?
- What other symptoms do you have?
- What other medical conditions do you have?
- What medications do you take?
The following tests may be done:
- Barium swallow
- Chest x-ray
- Esophageal pH monitoring (measures acid in the esophagus)
- Esophageal manometry (measures pressures in the esophagus)
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- Neck x-ray
Alternative Names
Dysphagia; Impaired swallowing
References
Orlando RC. Diseases of the esophagus. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D, eds. Cecil Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier;2007:chap 140.
Updated: 4/20/2012
Reviewed by: David C. Dugdale, III, MD, Professor of Medicine, Division of General Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine; and George F. Longstreth, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Kaiser Permanente Medical Care Program, San Diego, California. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
Notice: The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2012, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.